Home>diy>Architecture & Design>How To Draw A Floor Plan On Graph Paper

Architecture & Design
How To Draw A Floor Plan On Graph Paper
Modified: February 25, 2024
Learn how to draw a floor plan on graph paper with step-by-step instructions and tips for architecture design. Create your dream space efficiently and accurately.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Designing a floor plan is an essential part of any architectural or interior design project. It allows you to visualize the layout of a space and determine the placement of walls, doors, windows, and furniture. While there are many software programs available to create floor plans, sometimes going back to basics can be both fun and rewarding. In this article, we’ll show you how to draw a floor plan on graph paper, providing you with a hands-on approach to bring your design ideas to life.
Before we dive into the process, let’s discuss why drawing a floor plan on graph paper can be beneficial. Firstly, it allows you to have a bird’s eye view of the space, giving you a better understanding of the proportions and overall layout. Additionally, it helps you to develop your spatial awareness and visualization skills, which are valuable in the field of architecture and design. Furthermore, drawing on graph paper allows you to accurately measure and scale your floor plan, ensuring precise dimensions.
To get started with drawing your floor plan, there are a few materials that you’ll need. Firstly, you’ll need a large sheet of graph paper. This special kind of paper has a grid of equally spaced squares, which will help you create a scaled representation of your floor plan. You can easily find graph paper at most stationery or art supply stores. Additionally, you’ll need a ruler, a pencil, an eraser, and colored pencils or markers to add some visual flair to your floor plan.
Now that you have your materials ready, let’s move on to the step-by-step process of drawing a floor plan on graph paper. By following these steps, you’ll be able to create a detailed and accurate representation of your space, making it easier to plan furniture layouts, visualize traffic flow, and even estimate materials needed for construction or remodeling projects.
Key Takeaways:
- Drawing a floor plan on graph paper enhances spatial awareness and visualization skills, providing a bird’s eye view of the space and ensuring precise dimensions for accurate design representation.
- The hands-on approach of drawing a floor plan on graph paper allows for creativity, personalization, and a deeper understanding of spatial layout and flow, serving as a valuable resource for various design projects.
Materials needed
Before you begin drawing your floor plan on graph paper, it’s important to gather all the necessary materials. Having the right tools at hand will ensure a smooth and efficient process. Here’s a list of materials you’ll need:
- Large sheet of graph paper: Graph paper is essential for creating a scaled representation of your floor plan. Make sure to choose a sheet that is large enough to accommodate the size of your space.
- Ruler: A ruler is crucial for drawing straight lines and measuring distances accurately. Opt for a transparent ruler with both inches and centimeters for versatility.
- Pencil: A good quality pencil will allow you to create precise markings on the graph paper. It’s always a good idea to have an extra pencil or two in case one breaks or wears out.
- Eraser: Mistakes happen, and having a reliable eraser at hand will help you correct any errors without damaging the graph paper.
- Colored pencils or markers: While not necessary, colored pencils or markers can be used to distinguish different elements in your floor plan, such as walls, doors, windows, and furniture. They can add a visual appeal to the final drawing.
By having these materials ready, you’ll be fully equipped to embark on your floor plan drawing journey. Remember to choose high-quality materials that will withstand frequent use, as you may need to refer back to your floor plan throughout your design process.
Step 1: Measure the room
The first and most crucial step in drawing a floor plan on graph paper is to measure the dimensions of the room or space you want to design. Accurate measurements will ensure that your floor plan is scaled correctly and provides an accurate representation of the space.
Start by using a measuring tape to measure the length and width of the room. Measure from wall to wall, excluding any built-in furniture or fixtures. Record these measurements in units that are easy to work with, such as inches or centimeters.
To make your measurements even more accurate, it’s helpful to measure multiple points along each wall. This will account for any irregularities or angled walls, allowing you to create a more precise floor plan.
Once you have all the measurements, transfer them onto a separate sheet of paper or create a rough sketch. This will serve as a reference as you create your floor plan on the graph paper.
It’s important to note that when measuring and drawing your floor plan, you should consider the scale you want to use. The scale represents the proportional relationship between the measurements on your floor plan and the actual dimensions of the room. For example, 1 inch on the floor plan may represent 1 foot in real life. Choose a scale that allows you to fit the space on the graph paper while still providing enough detail.
Ultimately, taking accurate measurements is the foundation of a well-designed floor plan. It ensures that your drawings accurately represent the space and allows you to plan and visualize the layout effectively.
Step 2: Scale conversion
After you have measured the dimensions of the room, it’s time to convert those measurements into a scaled representation on the graph paper. Scale conversion is a critical step that allows you to accurately depict the room’s proportions and ensure that everything fits within the confines of the graph paper.
To determine the scale for your floor plan, you need to decide how many units of measurement on the graph paper will correspond to a specific measurement in real life. For example, you might decide that each square on the graph paper represents one foot of actual space. This means that a room that measures 20 feet by 15 feet would be represented by a rectangle that measures 20 squares by 15 squares on the graph paper.
To convert your measurements, you’ll need to calculate the ratio between the actual measurements and the scale you’ve chosen. Simply divide the actual measurement by the scale to find the corresponding measurement on the graph paper. For example, if your scale is 1 inch = 1 foot and your room measures 20 feet, the corresponding length on the graph paper would be 20 inches.
Using a ruler, draw the outer boundary of the room on the graph paper according to the converted measurements. Start by drawing the length of the room along one edge of the graph paper and then draw the width perpendicular to it. This will give you the basic shape of the room.
Remember to be precise with your measurements and use a straightedge to draw straight lines. Small inaccuracies can compound and affect the overall accuracy of the floor plan.
Scale conversion is a crucial step in creating a floor plan that accurately represents the dimensions of the room or space you’re designing. By ensuring that your floor plan is scaled correctly, you’ll be able to create a more realistic and practical representation of your design.
Step 3: Marking the graph paper
Now that you have your measurements converted to the appropriate scale, it’s time to mark the graph paper to create a grid that will serve as the foundation for your floor plan. This grid will allow you to accurately position walls, doors, windows, furniture, and other elements within the space.
Start by determining the size of the grid squares on your graph paper. This will depend on the scale you’ve chosen and the size of the room. For example, if you’ve selected a scale of 1 inch = 1 foot and your room is 20 feet long, you may decide to make each grid square on the graph paper equal to 2 inches. This will ensure that the entire length of the room fits within the grid.
Using your ruler, lightly draw horizontal and vertical lines on the graph paper to create a grid of squares based on the size you’ve chosen. Make sure the lines are faint and easily erasable, as they will serve as guidelines for drawing the walls and other elements.
Next, mark the corners of the room on the graph paper using small, dark dots. These dots will represent the precise locations where the walls will intersect. If there are any irregularities or angled walls in the room, mark those points as well.
Once you have marked the corners, use your ruler to connect the dots and draw the walls of the room. Start with the outer walls and then move on to dividing the space into rooms or areas according to your floor plan layout. Always ensure that the lines are straight and aligned with the grid.
If your room has any openings such as doors or windows, mark their locations on the graph paper as well. Use different symbols or colors to differentiate between doors, windows, and walls. This will make it easier to visualize and plan the flow and functionality of the space.
Once you have finished marking the graph paper, take a moment to review your work and make any necessary adjustments or corrections. Remember, the accuracy of your grid and markings will directly impact the accuracy of your final floor plan.
Marking the graph paper is an important step that sets the stage for creating a detailed and precise floor plan. By carefully marking the grid, you’ll be able to position walls, doors, windows, and furniture accurately, resulting in a well-designed and functional space.
When drawing a floor plan on graph paper, use a scale where each square represents a specific measurement (e.g. 1 square = 1 foot) to ensure accurate proportions.
Read more: How To Draw Chairs On A Floor Plan
Step 4: Walls and doors
With the graph paper marked and the grid set, it’s time to start drawing the walls and doors on your floor plan. This step will give shape to the rooms and define the layout of your space.
Begin by focusing on the outer walls of the room. Using your ruler, draw straight lines along the grid to connect the marked corners and create the structure of the walls. Make sure that the lines are aligned with the grid squares to ensure accuracy.
If you have interior walls that divide the space into separate rooms or areas, plan their positions based on your design concept. Use the same technique of drawing straight lines along the grid to represent these walls. Take into consideration the flow and functionality of the space as you position the interior walls.
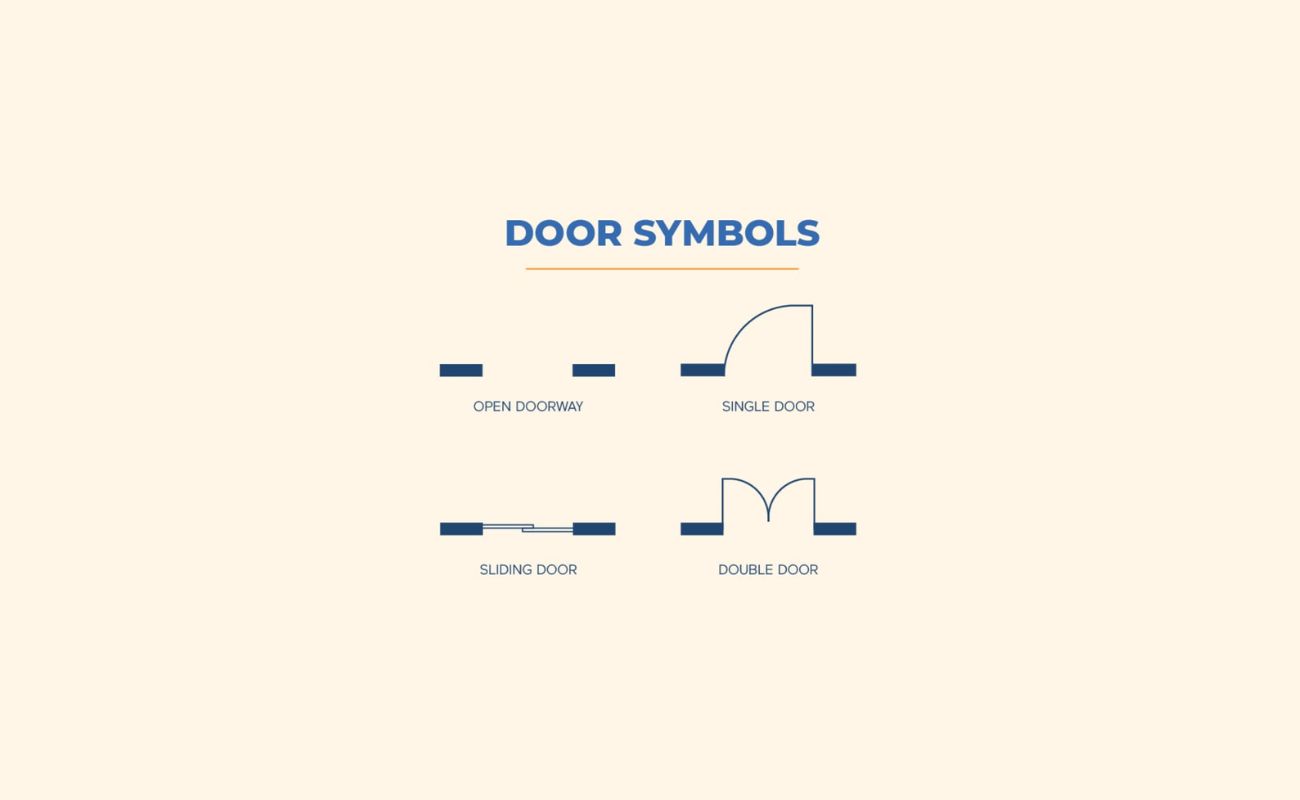
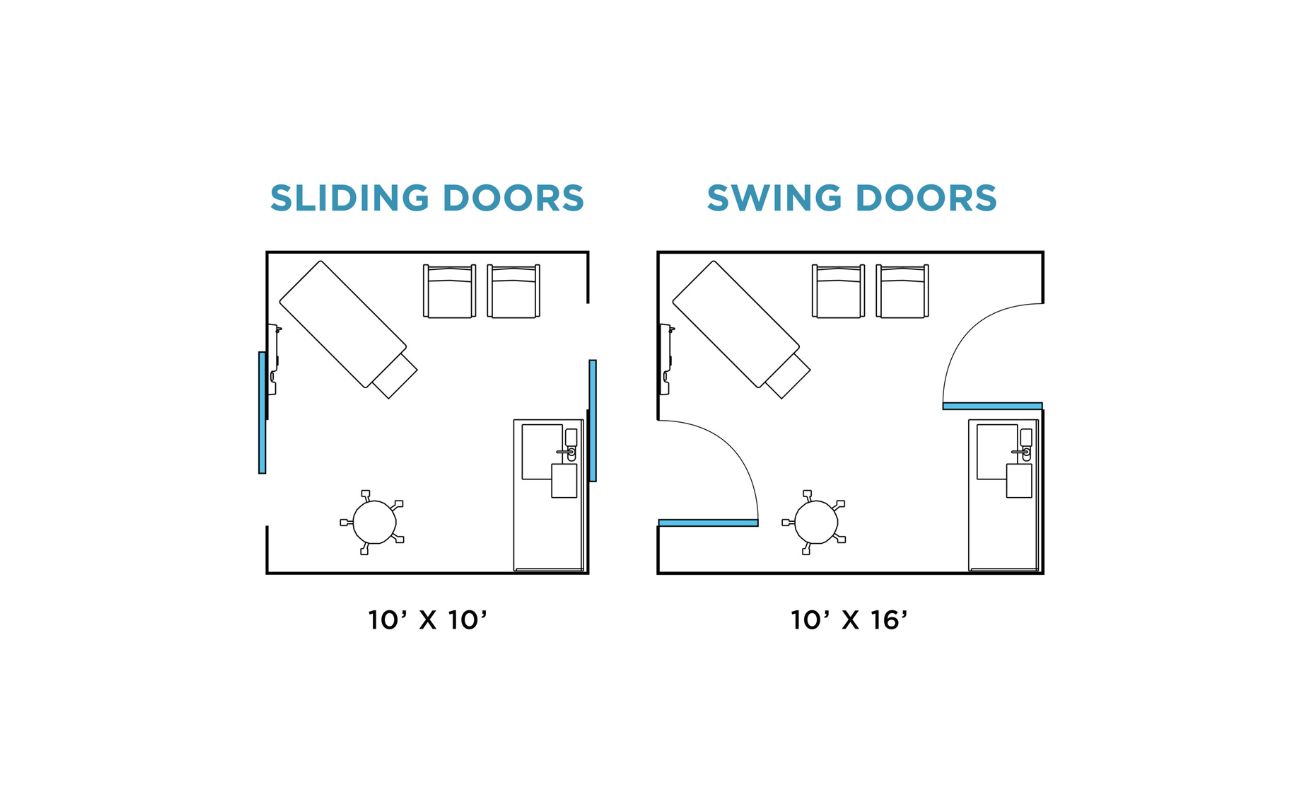
Next, it’s time to draw the doors on the floor plan. Start by determining the size and placement of each door. Remember to consider the swing of the door when positioning it. Using your ruler, draw lines to represent the width of the door, and indicate the direction of the swing with an arc or a curved line. Be consistent with your symbols or notations for doors throughout the floor plan.
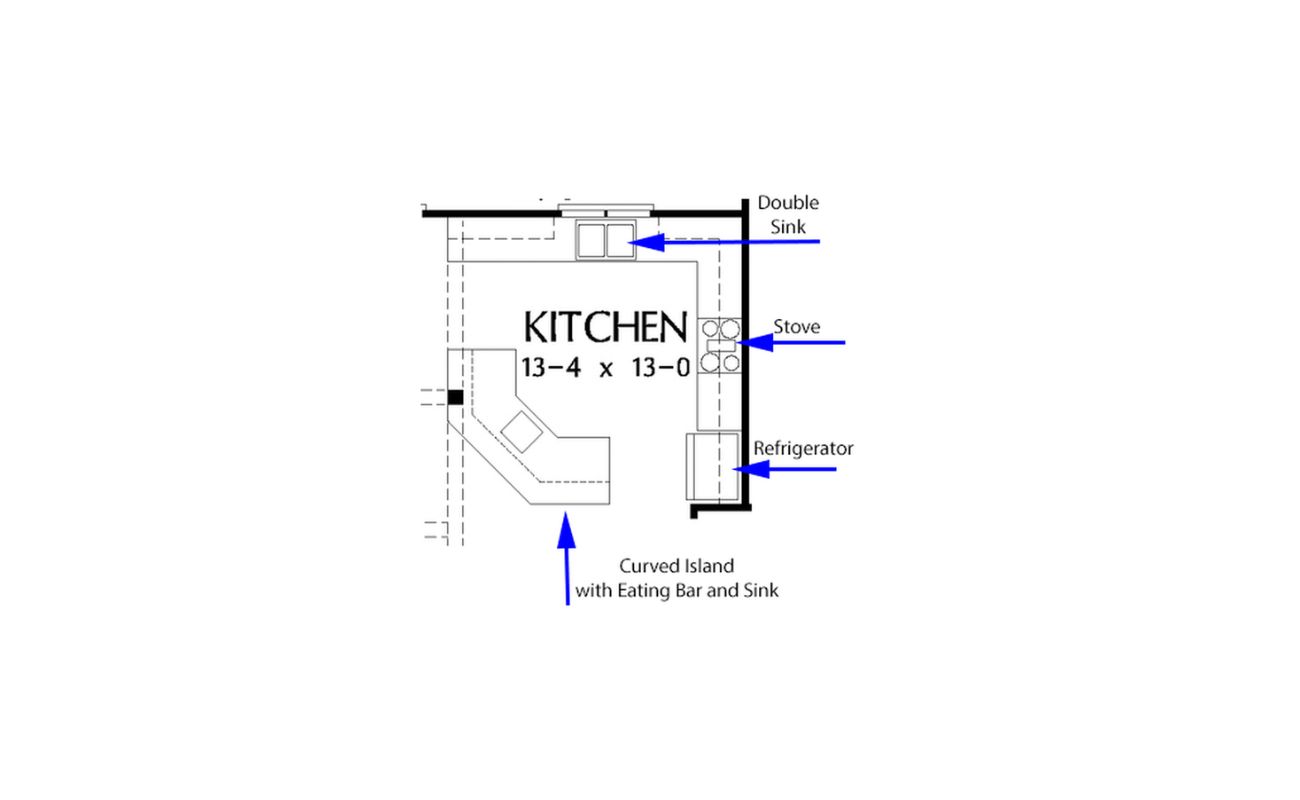
Be sure to include any additional elements that are part of the wall, such as windows, electrical outlets, or light switches. Use different symbols or colors to represent these elements and indicate their locations on the floor plan.
As you draw the walls and doors, take the opportunity to consider the traffic flow and functional layouts of the rooms. Imagine how people will move through the space and ensure that there is enough clearance for doors to open and furniture to be placed comfortably.
Remember to keep referring to your measurements and scale as you draw. Double-check the accuracy of your lines and measurements to ensure that your floor plan is as precise as possible.
By completing this step, you’ll have a clear visual representation of the walls and doors in your floor plan. This will provide a solid foundation for further detailing and designing the layout of your space.
Step 5: Windows and other fixtures
Now that you’ve drawn the walls and doors on your floor plan, it’s time to add the windows and other fixtures that will enhance the functionality and aesthetics of your space.
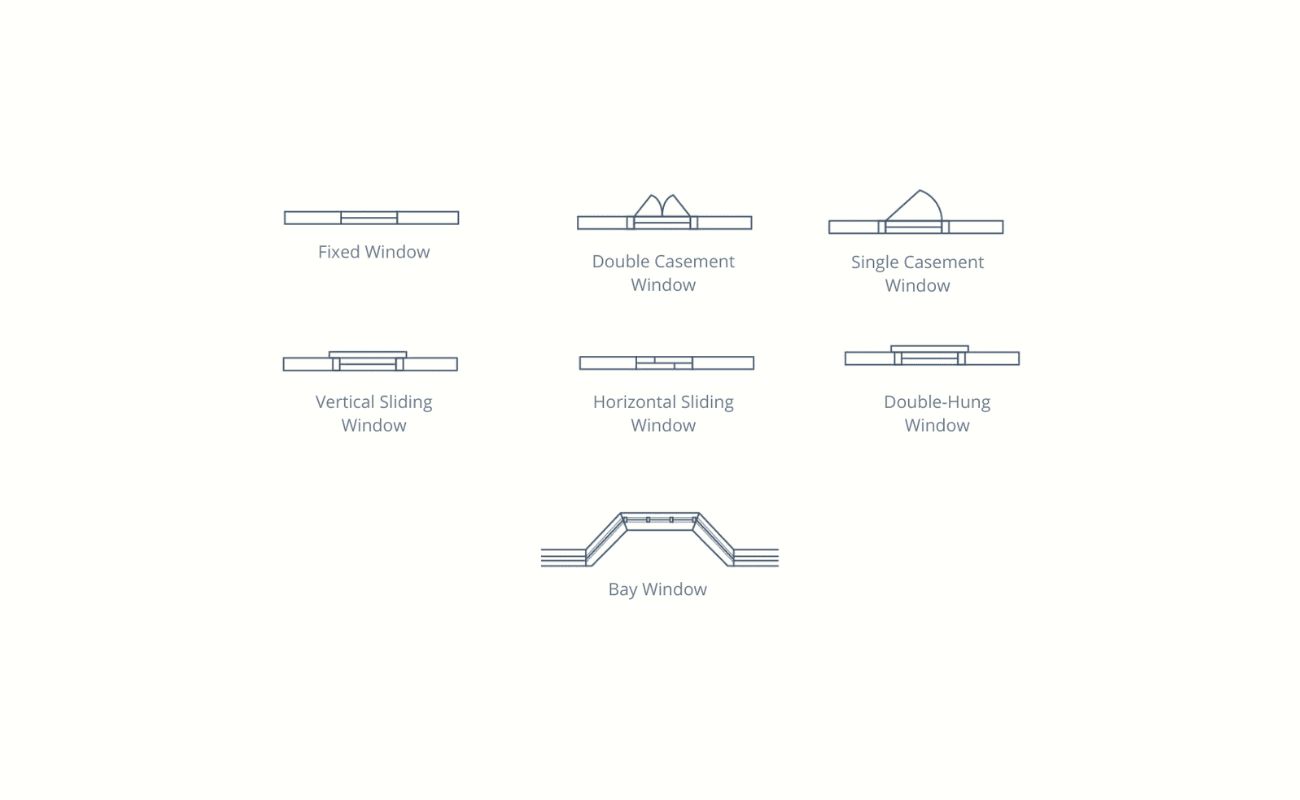
Start by determining the placement and size of each window. Consider factors such as natural light, views, and privacy. Using your ruler, draw rectangles or squares to represent the windows within the walls. Take note of the dimensions of the windows to ensure accuracy in your floor plan.
In addition to windows, you may have other fixtures in your space that need to be marked on the floor plan. These can include items such as built-in shelves, fireplace mantels, or decorative features. Use symbols or graphical representations to indicate these fixtures on the floor plan, ensuring that they are proportionally sized and positioned.
Consider the scale and style of these elements as you add them to your floor plan. This will help you visualize how they will contribute to the overall design and functionality of the space. Remember to refer back to your measurements to ensure the correct placement and dimensions of the fixtures.
Adding windows and other fixtures to your floor plan allows you to further refine the layout and aesthetics of your space. Consider how these elements will interact with the walls, doors, and overall design concept, ensuring a cohesive and well-designed floor plan.
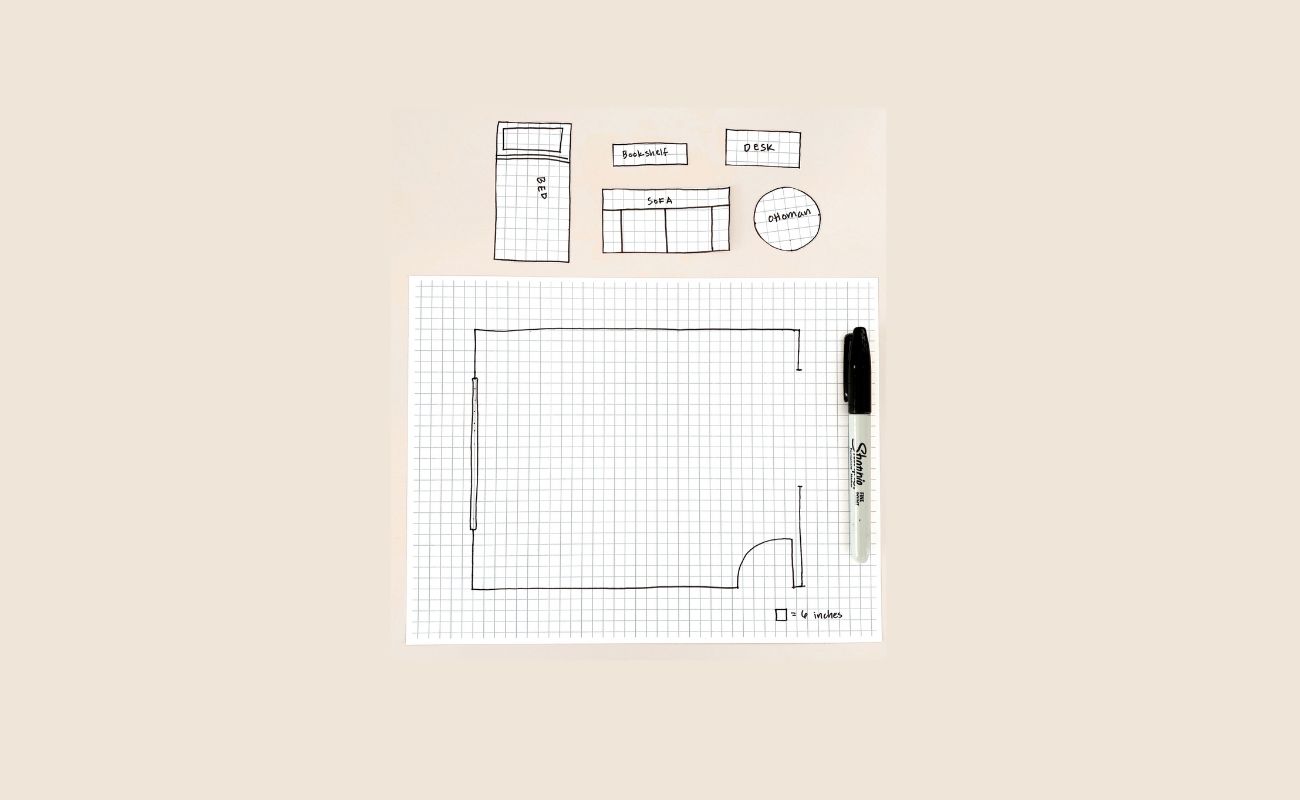
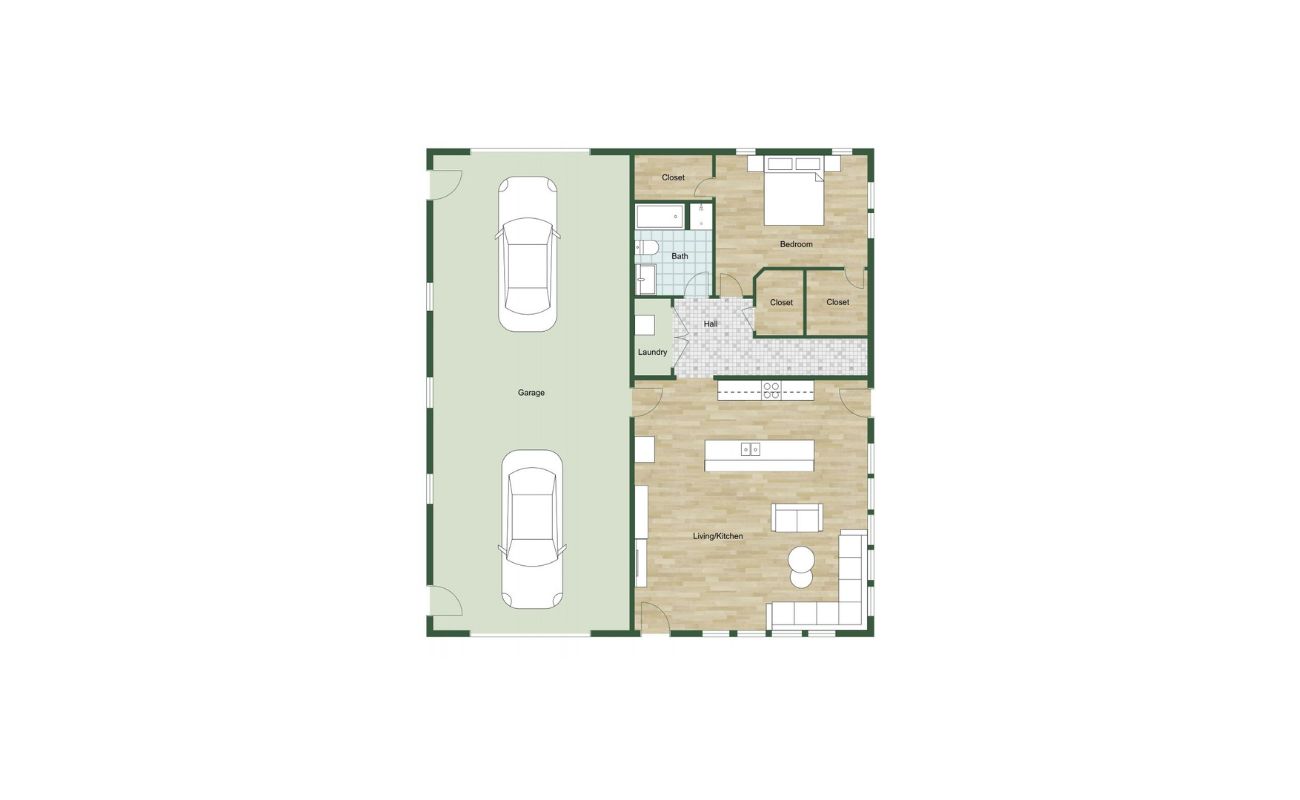
Step 6: Furniture placement
Now that you have the structural elements of your floor plan complete, it’s time to focus on furniture placement. This step will bring your design to life by considering the functionality, flow, and visual appeal of your space.
Start by envisioning the purpose of each room and the activities that will take place within it. Think about the size and style of the furniture pieces you plan to incorporate. This will help you determine the appropriate scale for each item and ensure that it fits within the room without creating overcrowding or blockages of movement.
Using a separate sheet of paper or tracing paper overlay, sketch out the outlines of furniture pieces scaled to match the grid on your floor plan. You can also use pre-made furniture templates available online or in design software. This will allow you to experiment with different furniture arrangements without permanently marking the floor plan.
Consider the functionality and flow of the space while placing the furniture. For example, ensure that seating areas are easily accessible and that there is ample space for movement around tables and chairs. Take into account focal points such as windows, fireplaces, or entertainment centers when positioning furniture.
Experiment with different furniture layouts to find the one that best suits your design vision. Don’t be afraid to move things around and make adjustments until you achieve the desired balance and functionality. Keep in mind that furniture placement can greatly impact the overall feel and function of a room, so take your time to find the right arrangement.
It’s important to consider the size and scale of the furniture in relation to the room and other elements. Ensure that the furniture pieces are proportionate to the space and do not overshadow or overpower the room’s design. Take note of any measurement restrictions or obstacles that may affect furniture placement, such as doorways or electrical outlets.
By finalizing the furniture placement in your floor plan, you will have a clear vision of how the space will function and flow. This step brings your design concept to life, helping you create a functional and inviting environment.
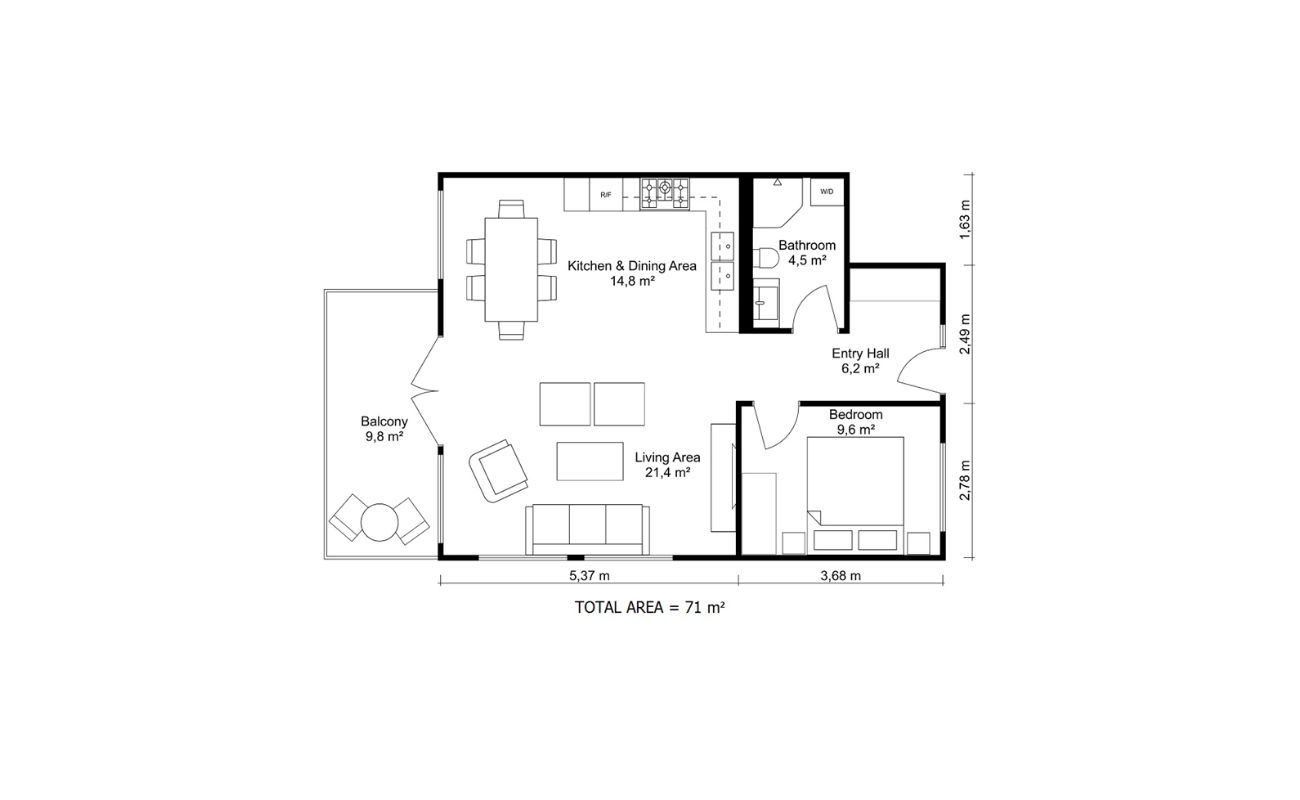
Step 7: Adding measurements and labels
In the final step of drawing your floor plan on graph paper, it’s essential to add the necessary measurements and labels to ensure clarity and understanding of the space. This step will provide crucial information for builders, contractors, and anyone who needs to interpret and work with your floor plan.
Start by adding measurements to the walls, doors, and windows. Use your ruler to draw straight lines with the measurements labeled next to them. Include both the length and width of each element to provide a complete understanding of the dimensions. If there are any irregular walls or angled features, be sure to indicate the measurements accordingly.
Next, add labels or symbols to identify each room or area on the floor plan. This will make it easier to reference specific spaces within the overall layout. You can use abbreviations or simple names to indicate the purpose of each room, such as “BR” for bedroom or “KIT” for kitchen.
Consider adding labels or symbols for the furniture pieces you’ve placed in the floor plan. This will provide a clear understanding of what each item represents and how it contributes to the overall design. You can use simple icons or abbreviations to indicate the type of furniture, such as “C” for chair or “TB” for table.
In addition to measurements and labels, you may want to include annotations or notes that provide additional information about specific elements or design choices. This can be helpful for conveying any special requirements or considerations to contractors or other professionals who will be working with your floor plan.
Finally, take a moment to review your floor plan and ensure that all measurements, labels, and annotations are accurate and clear. Cross-check the dimensions to make sure they align with your initial measurements and design intent. Erase any unnecessary lines or markings to maintain a clean and professional appearance.
By adding measurements and labels, you will enhance the functionality and comprehensibility of your floor plan. This step ensures that anyone who views the plan can understand the spatial relationships, dimensions, and purpose of each area, allowing for smoother communication throughout the design and construction process.
Read more: How To Draw A Shower On A Floor Plan
Conclusion
Congratulations! You’ve successfully learned how to draw a floor plan on graph paper. By following the step-by-step process, you’ve created a detailed and accurate representation of your space, allowing you to visualize the layout, placement of walls, doors, windows, and furniture.
Drawing a floor plan on graph paper provides numerous benefits. It allows you to have a bird’s eye view of the space, aiding in spatial awareness and visualization skills. Additionally, it provides a scaled representation, ensuring precise dimensions and measurements. This hands-on approach allows you to bring your design ideas to life and develop a deeper understanding of the spatial layout and flow.
Remember, accurate measurements, proper scale conversion, marking the graph paper, and drawing the walls, doors, windows, furniture, and other fixtures are all vital components of creating a comprehensive floor plan. Take your time, be precise, and consult your measurements regularly to ensure an accurate representation.
The floor plan you’ve created can serve as a foundation for various design projects, including interior design, architecture, remodeling, or space planning. It can be a valuable resource when communicating your design ideas to professionals or contractors involved in the project.
Incorporate personal touches and creativity to make your floor plan truly unique. Consider using color, shading, or texture to enhance the visual appeal and make certain elements stand out. This will add an extra touch of professionalism and help convey your design vision effectively.
Now that you have a beautifully drawn floor plan, you can move forward with confidence in your design process. Whether you’re redesigning your home, creating a new office layout, or planning a renovation project, this floor plan will provide a solid foundation for your design decisions.
Remember, practice makes perfect! The more you engage with drawing floor plans on graph paper, the more adept you will become at visualizing and transforming your ideas into detailed representations. So, keep honing your skills, experimenting with different layouts and styles, and enjoy the rewarding process of bringing your design visions to life.
Frequently Asked Questions about How To Draw A Floor Plan On Graph Paper
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.



0 thoughts on “How To Draw A Floor Plan On Graph Paper”