Home>diy>Architecture & Design>How To Scale Floor Plan


Architecture & Design
How To Scale Floor Plan
Modified: March 6, 2024
Discover how to efficiently scale your floor plan with expert architecture design tips and techniques. Enhance your space and create a functional layout with our step-by-step guide.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
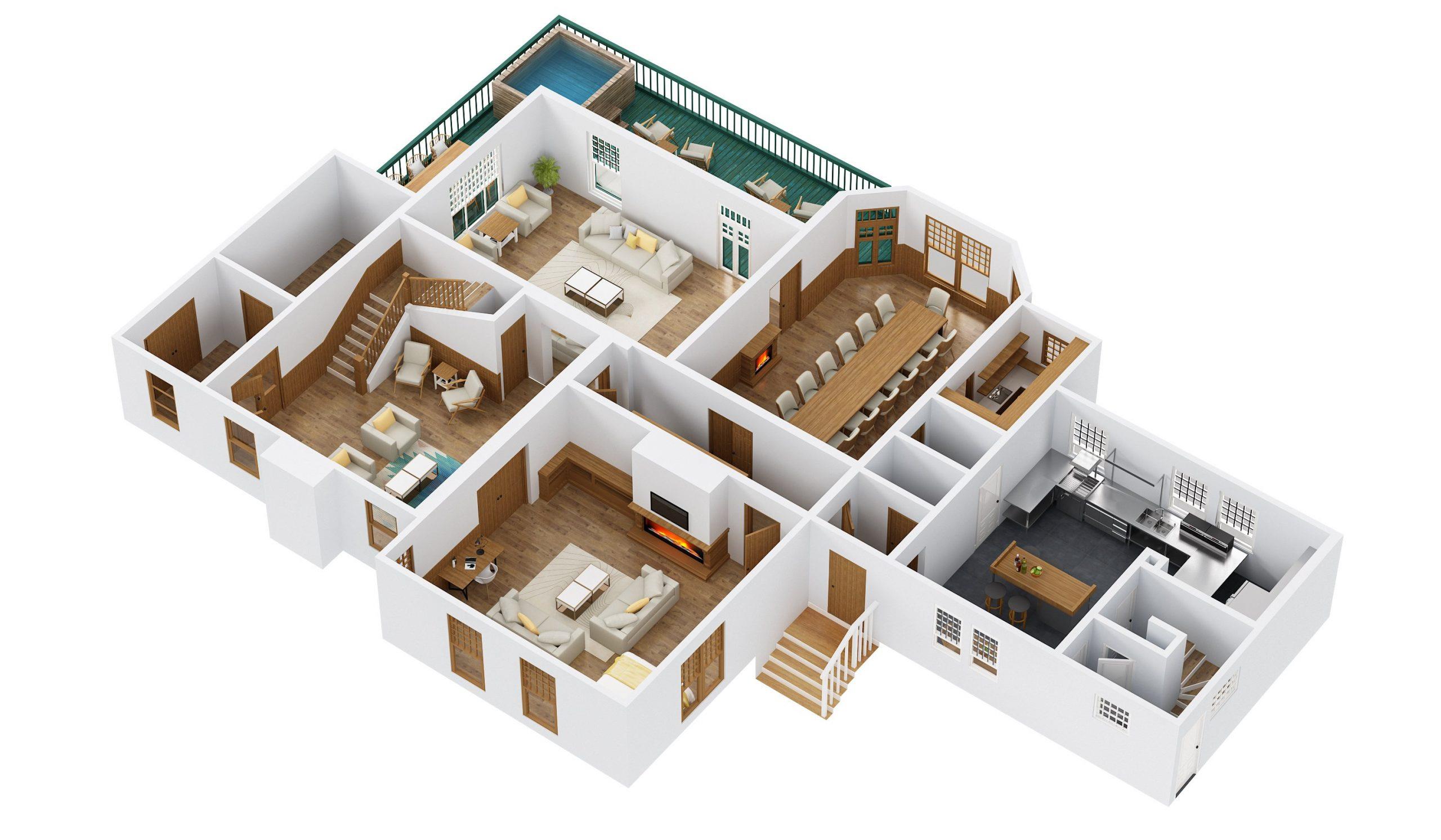
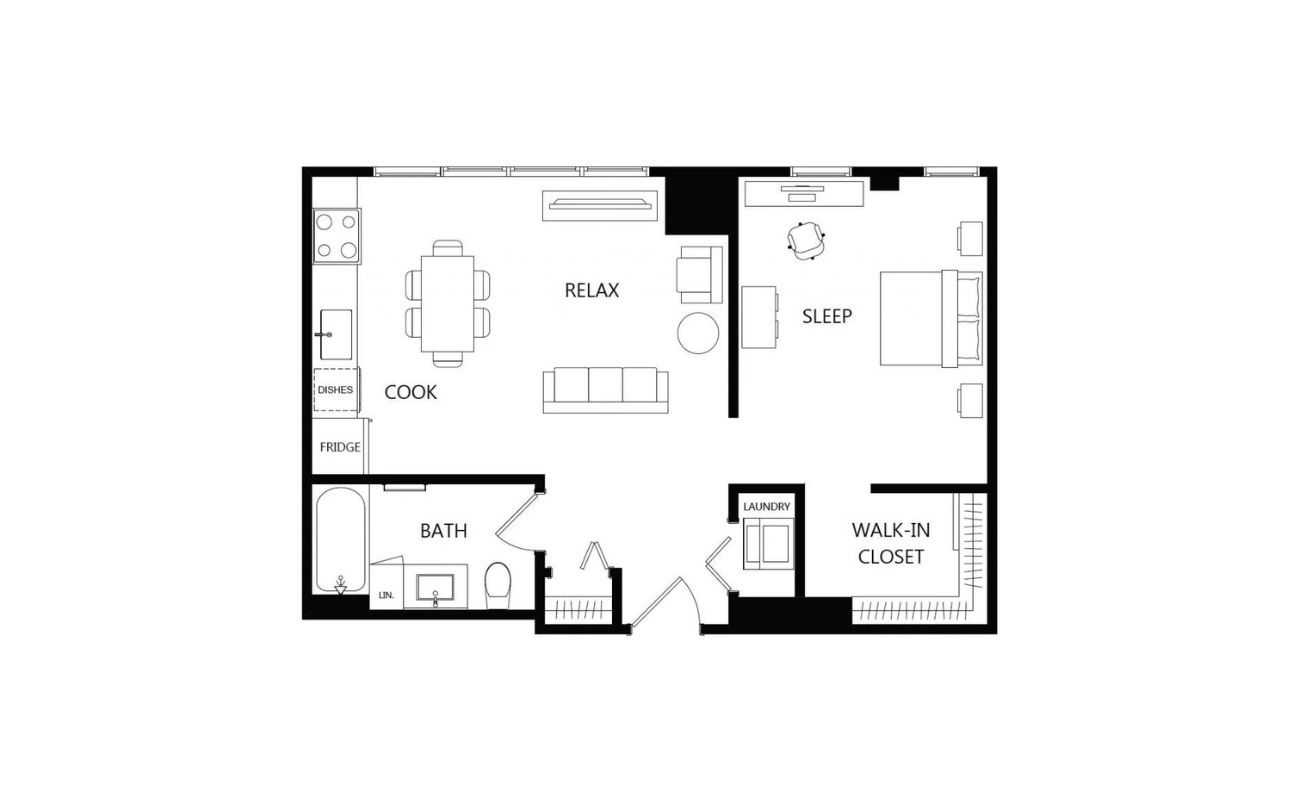
When it comes to designing a space, be it a new home, an office, or a renovation project, having a scaled floor plan is crucial. A floor plan is a visual representation of a space, showing the layout, dimensions, and features of the area. Scaling the floor plan accurately ensures that all elements are properly proportioned and aligned, making it easier for architects, designers, and contractors to work with.
In this article, we will guide you through the process of scaling a floor plan. We will cover everything from understanding different scales to measuring dimensions, calculating scaling ratios, transferring measurements to graph paper, and finally drawing the scaled floor plan. So, whether you’re a homeowner looking to visualize your dream home or a professional designer wanting to bring your ideas to life, this step-by-step guide will help you scale your floor plans effectively.
Key Takeaways:
- Scaling a floor plan involves determining the right scale, measuring accurately, and transferring dimensions to graph paper. Attention to detail and precision are crucial for creating an accurate visual representation of a space.
- Choosing the appropriate scale, using the right tools for measurement, and paying attention to details like doors, windows, and furniture placements are essential for creating a scaled floor plan that accurately reflects the real-world space.
Read more: How To Dimension A Floor Plan
Step 1: Determine the desired scale
Before you begin scaling your floor plan, it’s essential to determine the desired scale. The scale represents the ratio between the dimensions of the real-world space and the dimensions of your scaled drawing. It determines how much you will shrink or enlarge the floor plan to fit on a sheet of paper.
Understanding different scales:
- 1:50 scale – This scale means that 1 unit on the drawing represents 50 units in real life. It is commonly used for large-scale projects like commercial buildings or urban plans.
- 1:100 scale – Here, 1 unit on the drawing represents 100 units in reality. It is often used for medium-sized projects such as homes or small office spaces.
- 1:200 scale – This scale represents 1 unit on the drawing as 200 units in real life. It is frequently used for smaller projects like apartments or individual rooms.
Choosing the appropriate scale for your floor plan depends on the size of the space and the level of detail you need to include. Larger spaces with many features may require a smaller scale to fit everything accurately, while smaller spaces can be adequately represented with a larger scale.
Consider the purpose of the floor plan and the level of detail you need to convey. If it’s for architectural or interior design purposes, you may need to opt for a smaller scale to include intricate details like furniture placements and precise measurements. If the floor plan serves a more general purpose, such as conveying the overall layout of a space, a larger scale might suffice.
Ultimately, the choice of scale should balance accuracy and clarity. It is important to ensure that the scaled floor plan is easy to read and understand, while still providing accurate measurements and representations of the space.
Step 2: Measure the dimensions of the floor plan
Once you have determined the desired scale for your floor plan, the next step is to measure the dimensions of the space accurately. This step is crucial in ensuring that the scaled floor plan is an accurate representation of the real-world space.
Tools needed for accurate measurements:
- Tape measure – A flexible tape measure is essential for measuring distances, such as the length and width of rooms, hallways, and other areas.
- Laser measure – Using a laser measure can help you accurately measure longer distances or areas that are difficult to reach.
- Angle finder – An angle finder is handy for measuring the angles between walls or other architectural features.
Techniques for measuring different areas of the floor plan:
- Rooms – Measure the length and width of each room, starting from the exterior walls. Note any architectural features like alcoves, bay windows, or built-in shelves.
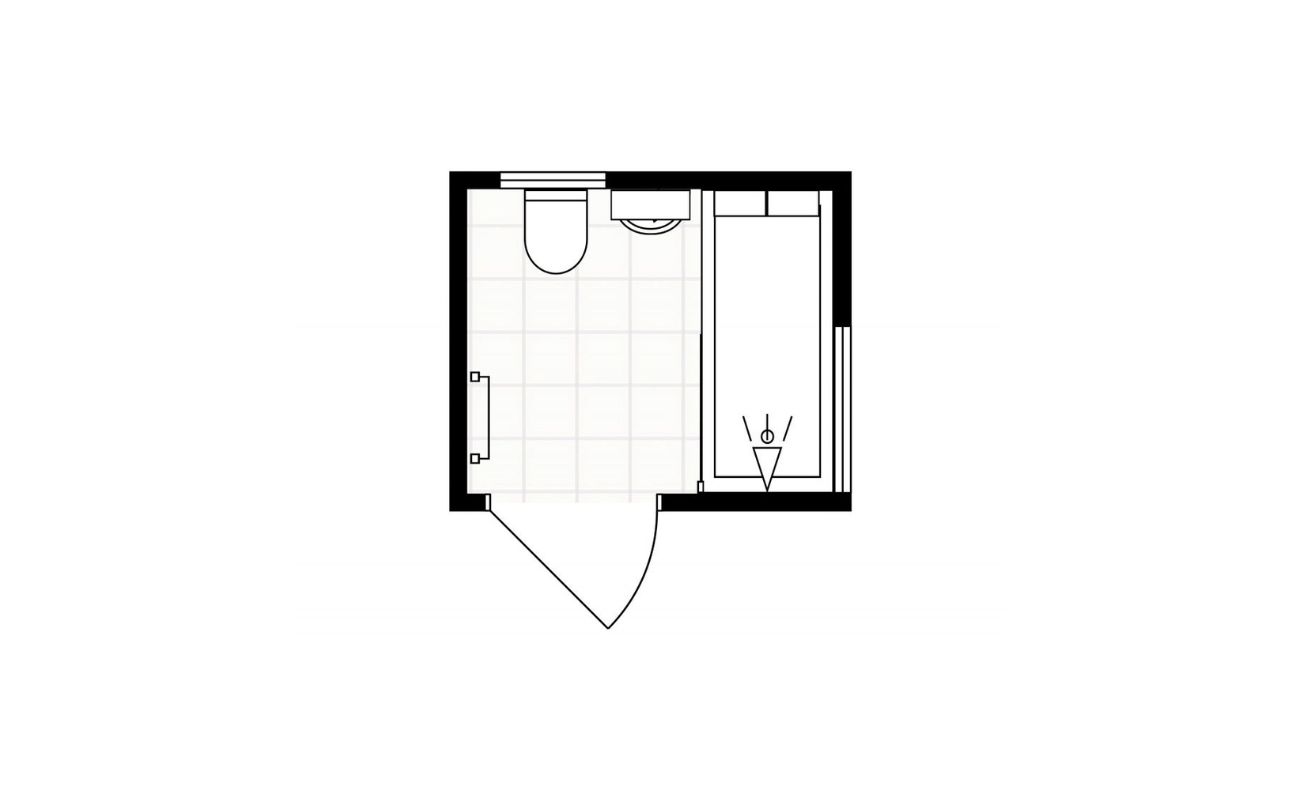
- Windows and doors – Measure the height, width, and distance from the edges of walls for windows and doors. Include any relevant information, such as the swing direction for doors.
- Walls – Measure the length of each wall, including any corners or irregularities in the shape. Note the position of electrical outlets, light switches, and any other fixtures.
- Closets and storage areas – Measure the dimensions of closets and storage spaces, including the height, width, and depth. Note any shelves or hanging rods inside.
- Stairs and hallways – Measure the width and length of staircases and hallways, including any landings or turns.
While measuring, be attentive to detail, and ensure that you are accurate in recording the dimensions. Double-check your measurements to avoid any errors that could affect the accuracy of the scaled floor plan.
Step 3: Calculate the scaling ratio
Once you have measured the dimensions of the floor plan, the next step is to calculate the scaling ratio. The scaling ratio is the relationship between the actual size of the space and the size of the scaled drawing.
Using the measured dimensions to calculate the scaling ratio:
To calculate the scaling ratio, you need to determine the conversion factor between the real-world measurements and the scaled drawing. Here’s how:
- Choose a reference dimension on the floor plan that is easy to measure, such as the width of a room or the length of a wall.
- Divide the actual measurement by the scaled measurement. For example, if the width of the room is 10 meters in reality and the scaled width on the drawing is 5 centimeters, divide 10 meters by 0.05 meters (convert centimeters to meters).
- The result of the division will give you the scaling ratio. In this example, the scaling ratio will be 200 (10 meters divided by 0.05 meters).
Examples of scaling ratios for common floor plan sizes:
- For a 1:50 scale – The scaling ratio would be 50. This means that 1 unit on the scaled drawing represents 50 units in real life.
- For a 1:100 scale – The scaling ratio would be 100. Here, 1 unit on the scaled drawing represents 100 units in reality.
- For a 1:200 scale – The scaling ratio would be 200. This scale represents 1 unit on the scaled drawing as 200 units in real life.
The scaling ratio is important as it determines how much the floor plan will be reduced or enlarged. It ensures that the scaled drawing accurately represents the dimensions of the real-world space.
By calculating the scaling ratio, you can ensure that your scaled floor plan is proportionate and consistent throughout.
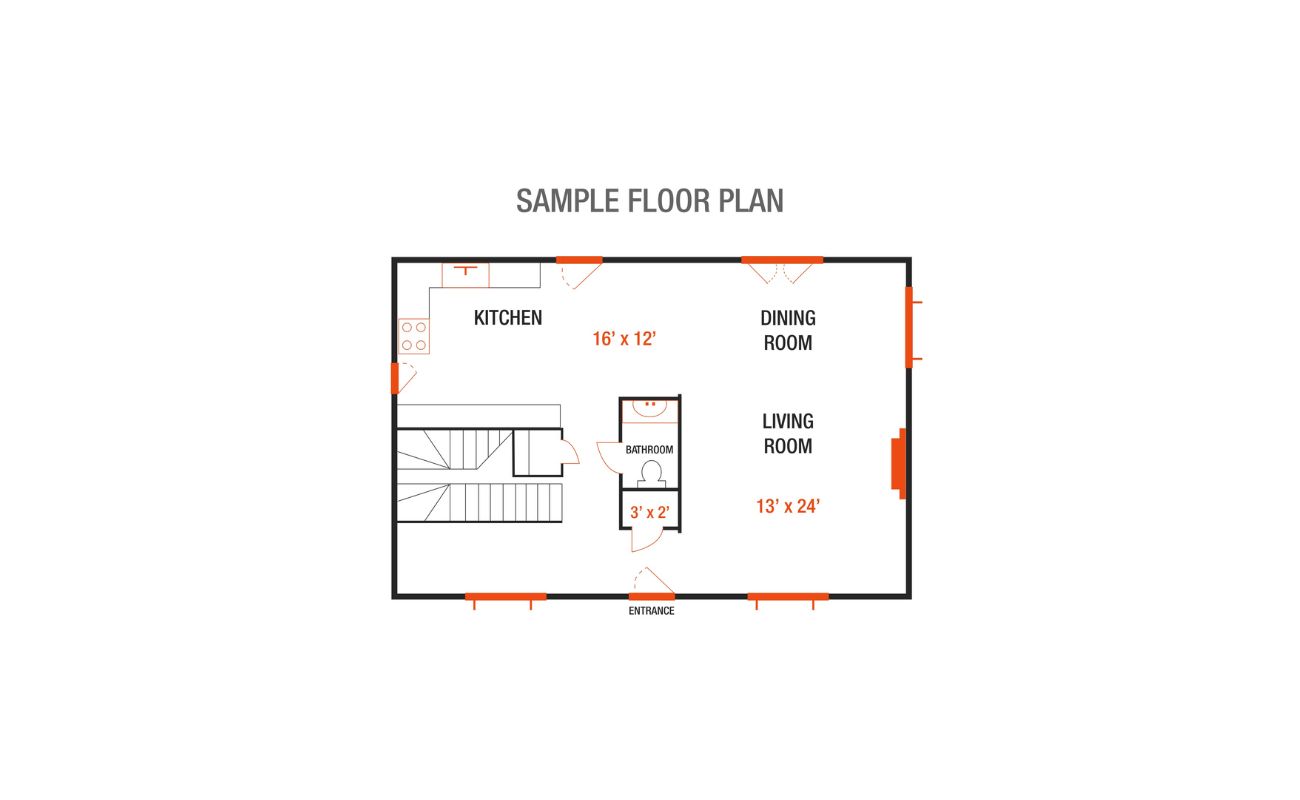
Step 4: Transfer the measurements to graph paper
Once you have calculated the scaling ratio, the next step is to transfer the measurements from the real-world floor plan to graph paper. This will allow you to create a scaled drawing that accurately represents the space.
Selecting the right graph paper:
It is important to choose graph paper that matches the scale of your floor plan. Look for graph paper with a grid that aligns with your desired scale. For example, if you are using a 1:50 scale, look for graph paper with a 1 cm grid that represents 50 cm in real life.
Transferring the measurements accurately and proportionally:
- Start by drawing the outline of the floor plan on the graph paper, using the scaling ratio you calculated. Make sure to maintain the same proportions and angles as the real-world floor plan.
- Use a straightedge to draw straight lines for walls, windows, and doors. Pay attention to their relative positions and dimensions.
- Measure and mark the dimensions of each room, wall, window, or door, and then transfer them to the graph paper. Use the scaling ratio to convert the real-world measurements to the scaled measurements.
- Include any other architectural features such as stairs, closets, or storage areas. Measure and mark their dimensions accurately.
As you transfer the measurements, it’s important to maintain accuracy and proportionality. Take your time to ensure that the scaled drawing accurately represents the real-world floor plan. Use a ruler or scale ruler to make precise measurements and straight lines.
Remember to label each element on the scaled drawing for easy identification.
Transferring the measurements to graph paper allows you to create a visual representation of the floor plan that accurately reflects the proportions of the space. It is a crucial step in creating a scaled floor plan that can be easily interpreted and understood.
When scaling a floor plan, use a scale ruler to accurately measure and convert dimensions from the plan to the actual space. This will ensure that the final design is proportional and to scale.
Read more: How To Choose A Floor Plan
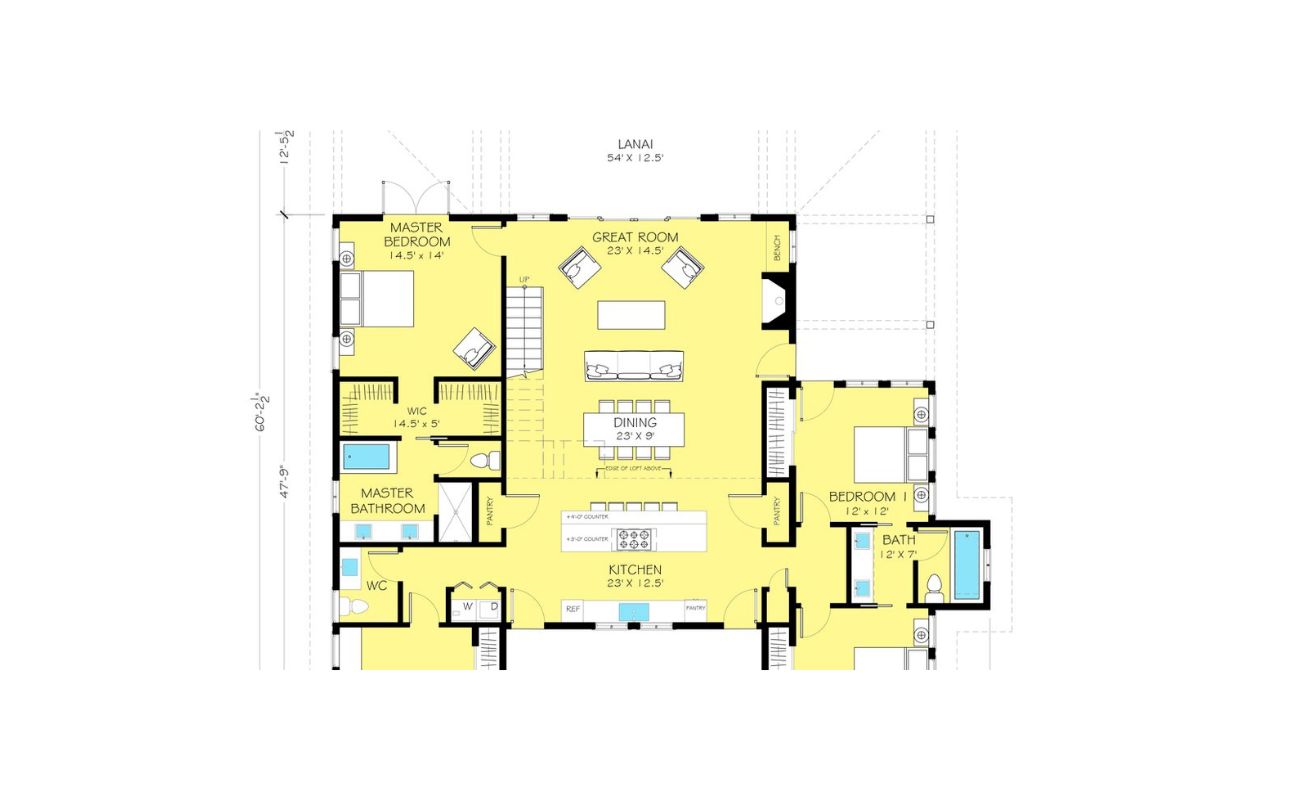
Step 5: Draw the scaled floor plan
With the measurements transferred to graph paper, it’s time to draw the scaled floor plan. This step involves using a scale ruler to create the scaled version of the floor plan and ensuring that all the details are accurately represented.
Using a scale ruler to create the scaled version:
- Choose a scale ruler that matches the scale of your floor plan. It should align with the scaling ratio you calculated earlier.
- Start by drawing the outline of the floor plan, using the scale ruler for precise measurements. Use straight lines to represent walls, and be mindful of angles and proportions.
- Continue drawing the floor plan by adding doors, windows, and other architectural features. Use the scale ruler to accurately represent their dimensions, positions, and relative distances from walls.
- Include any additional elements such as furniture placements, fixtures, or room labels. Make sure they are proportionate to the scale of the floor plan.
Taking care of details like doors, windows, and furniture placements:
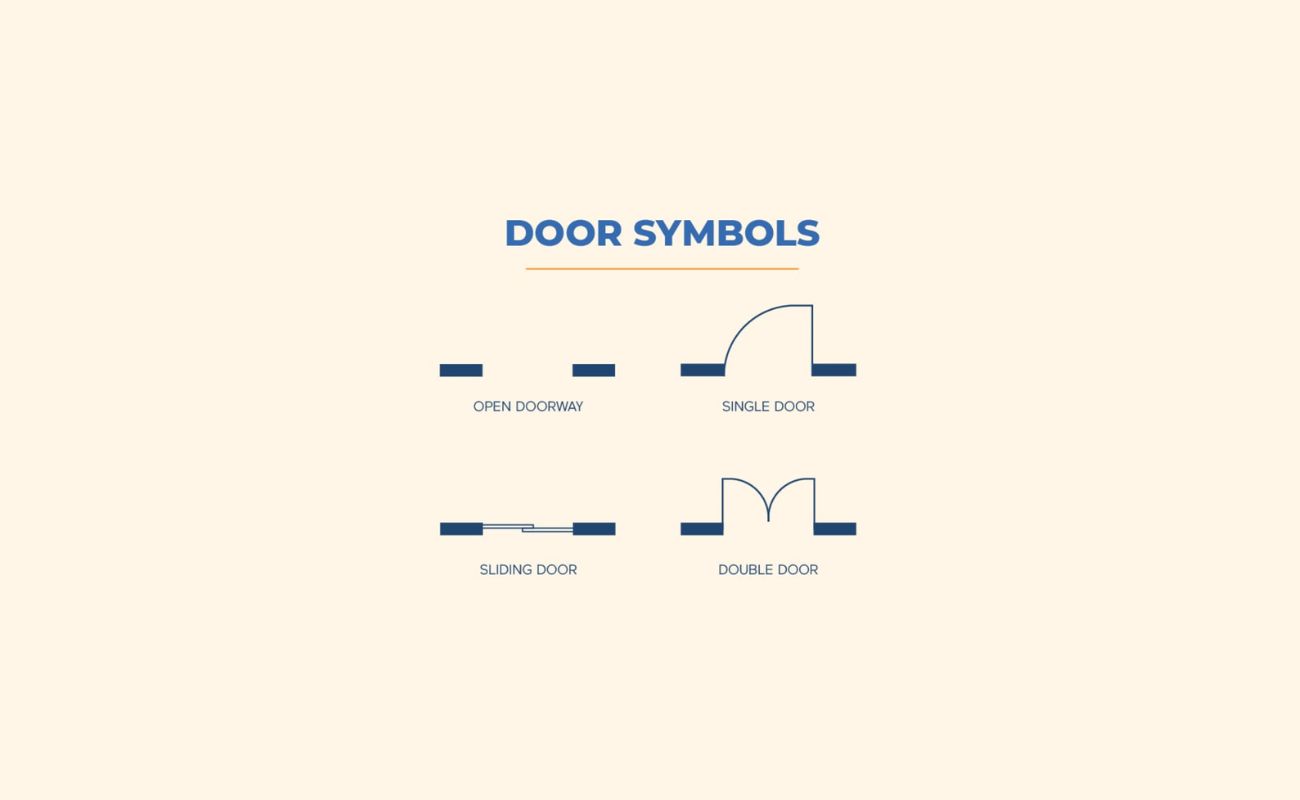
- Doors: Draw doors as rectangles, making sure to indicate which way they swing and their dimensions. Use the scale ruler to maintain accuracy.
- Windows: Draw windows as rectangles, representing their dimensions accurately. Indicate their position and size on the floor plan.
- Furniture placements: Use symbols or simple shapes to represent furniture items. Place them proportionally within each room, considering factors like flow and function.
Pay attention to the finer details while drawing the scaled floor plan. Accuracy is crucial in capturing the dimensions and proportions of the real-world space. Use the scale ruler consistently throughout the process to ensure that every element is correctly scaled.
By taking care of details like doors, windows, and furniture placements, you can create a comprehensive floor plan that provides a clear representation of the space and its layout.
Step 6: Revise and refine the scaled floor plan
After drawing the scaled floor plan, it’s important to take the time to revise and refine the drawing. This step involves checking for accuracy, making necessary adjustments, and adding labels and legends for easy understanding.
Checking for accuracy and making necessary adjustments:
- Double-check the measurements and proportions of the scaled floor plan. Compare them with the original measurements to ensure accuracy.
- Look for any inconsistencies or discrepancies in the drawing. Rectify any errors or discrepancies by making necessary adjustments.
- Ensure that all the elements, such as walls, doors, windows, and furniture, are correctly represented and align with the dimensions and positions from the real-world floor plan.
Adding labels and legends for easy understanding:
- Add labels to each room, indicating their purpose, such as “bedroom,” “kitchen,” or “living room.” This helps viewers understand the function of each area.
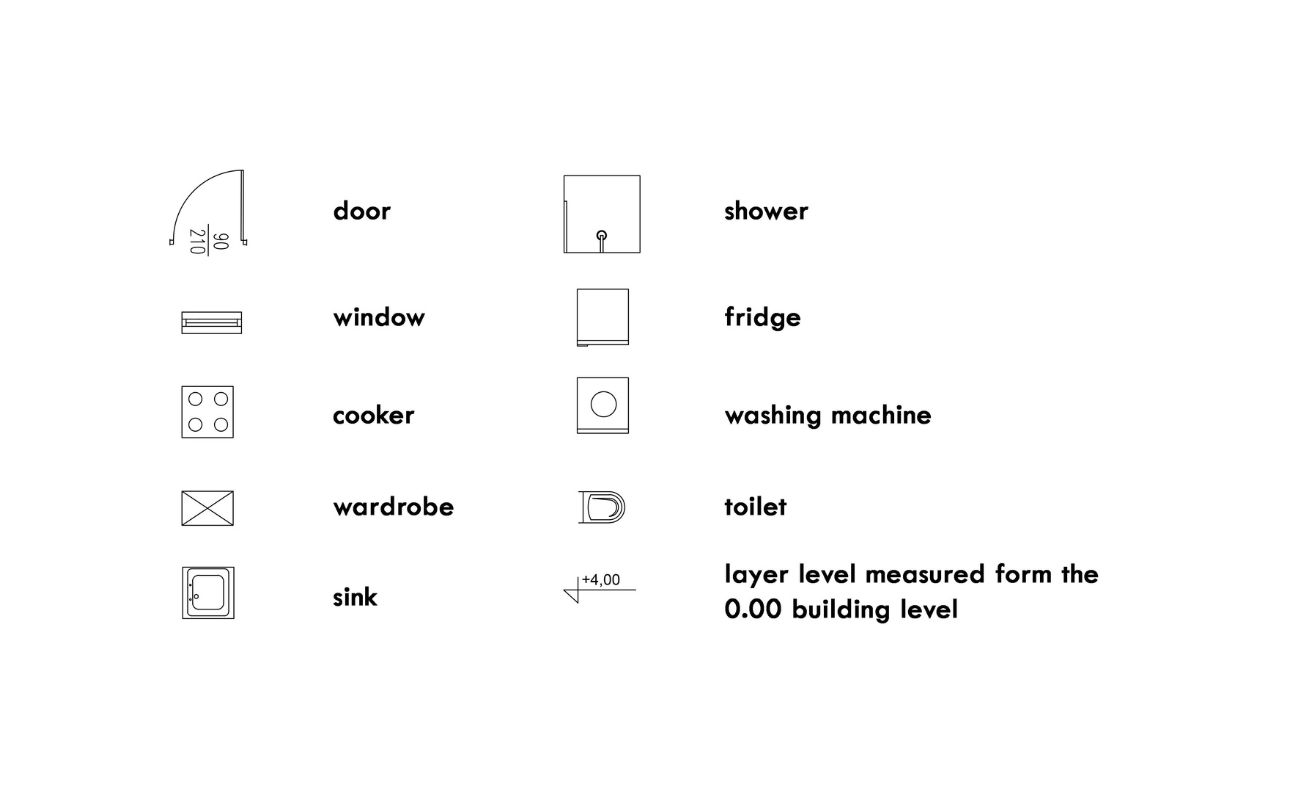
- Include a legend or key that defines the symbols used in the floor plan. This helps viewers easily identify and understand the various elements, such as doors, windows, and furniture placements.
- Consider adding additional information or notes, such as measurements, special features, or specific design choices. This makes the floor plan more informative and complete.
By revising and refining the scaled floor plan, you ensure that it accurately represents the real-world space. Checking for accuracy and making necessary adjustments helps eliminate any inaccuracies or inconsistencies. Adding labels and legends enhances the understanding and usability of the floor plan for both professionals and individuals viewing it.
Step 7: Review and finalize the scaled floor plan
The final step in scaling a floor plan is to review and finalize the drawing. This involves double-checking measurements and proportions, as well as making any final touches or alterations to ensure the accuracy and completeness of the scaled floor plan.
Double-checking measurements and proportions:
- Take the time to carefully review each element of the scaled floor plan, including walls, doors, windows, and furniture placements.
- Verify that the measurements accurately represent the dimensions of the real-world space, and that they align with the scaling ratio.
- Check the proportions of each element to ensure they are in proportion with the overall floor plan.
Making any final touches or alterations:
- If you spot any errors or inconsistencies during the review process, make the necessary alterations to correct them.
- Pay attention to small details, such as ensuring that symbols for doors and windows are accurately depicted with the correct dimensions and swing direction.
- Consider adding finishing touches, such as shading or color, to enhance the visual appeal of the scaled floor plan.
During the review and finalization phase, it’s important to have a critical eye and attention to detail. By thoroughly examining the scaled floor plan, you can identify any remaining errors or areas that require improvement. Making any necessary final touches or alterations will result in a polished and professionally presented scaled floor plan.
Once you are satisfied with the accuracy, proportions, and overall quality of the scaled floor plan, it is ready for use in architectural or design projects, presentations, or any other purposes that require an accurate visualization of the space.
Conclusion
Scaling a floor plan is a fundamental step in architectural and design processes, allowing for accurate representations of spaces. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can create a scaled floor plan that captures the dimensions, proportions, and features of a real-world space.
Throughout the process, it’s crucial to consider the desired scale, select the appropriate tools for measuring, calculate the scaling ratio, transfer measurements to graph paper accurately, and draw the scaled floor plan with attention to details like doors, windows, and furniture placements. Additionally, revising and refining the drawing, double-checking measurements and proportions, and making any necessary adjustments are essential to ensure accuracy.
By following these steps, you can create a scaled floor plan that serves as a valuable tool for architects, designers, contractors, and homeowners. A scaled floor plan provides a visual representation of the space, enhances communication, and aids in the decision-making process.
Remember, accuracy and attention to detail are critical throughout the scaling process. Taking the time to measure accurately, calculate the scaling ratio meticulously, and transfer measurements skillfully will result in a floor plan that accurately reflects the real-world space.
Whether you’re embarking on a home renovation, designing a commercial space, or simply visualizing your dream space, scaling a floor plan will help bring your ideas to life. So, grab your measuring tools, graph paper, and scale ruler, and start scaling your floor plans with confidence and precision.
Frequently Asked Questions about How To Scale Floor Plan
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.






0 thoughts on “How To Scale Floor Plan”